
A compound found in algae can have a significant role in cloud formation, and is said to be ‘a major source of climate-cooling gases’. A study author suggests a ‘need to rethink’ what the climate impacts are.
– – –
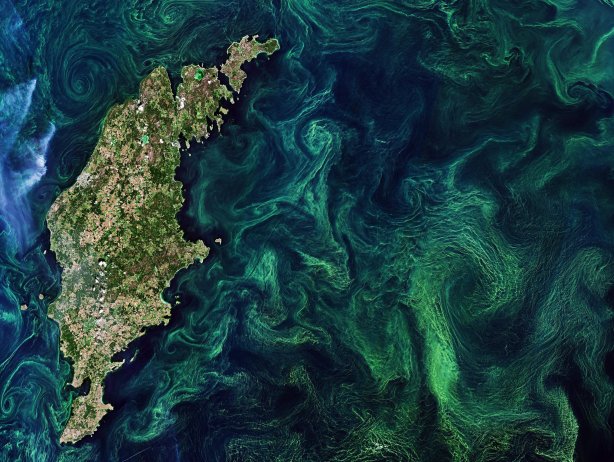
A common type of ocean algae plays a significant role in producing a massively abundant compound that helps cool the Earth’s climate, new research has discovered.
The findings of the study by the University of East Anglia (UEA) and Ocean University of China (OUC) could change our understanding of how these tiny marine organisms impact our planet, says Phys.org.
The work appears in Nature Microbiology.
The team identified the bloom-forming Pelagophyceae algae as potentially abundant and important producers of a compound called dimethylsulfoniopropionate, or DMSP.
Co-lead author Professor Jonathan Todd, of UEA’s School of Biological Sciences, said, “The Pelagophyceae are among the most abundant algae on Earth, yet they were not previously known as important producers of DMSP. This discovery is exciting because DMSP is an abundant antistress compound, food source for other microorganisms and major source of climate-cooling gases.”
Dr. Jinyan Wang, OUC/UEA Ph.D. student and first author, said, “Understanding the role of Pelagophyceae in DMSP production means we need to rethink how much of this compound is being produced and how it impacts our climate.”
Every year, billions of tons of DMSP are produced in the Earth’s oceans by marine microorganisms, helping them to survive by protecting against various stresses like changes in salinity, cold, high pressure, and oxidative stress.
Importantly, DMSP is the main source of a climate active gas called dimethylsulfide (DMS), which is known as the smell of the seaside.
This study suggests that DMSP production, and consequently DMS release, is likely higher than previously predicted and emphasizes the key role of microbes in regulating global climate. DMS also acts as a signaling molecule, guiding marine organisms to their food and deterring predators.
When DMS is released into the atmosphere, DMS oxidation products help form clouds which reflect sunlight away from the Earth, effectively cooling the planet.
This natural process is essential for regulating the Earth’s climate and is also hugely important for the global sulfur cycle, representing the main route by which sulfur from the oceans is returned to land.
. . .
The researchers say further study of Pelagophyceae algae in their natural environment is needed, as well as more detailed studies on other marine organisms.
Better measurements of environmental DMSP levels, production and breakdown rates, and the abundance of the enzymes involved in making DMSP are also critical to further advance the field.
Full report here.
– – –
Image: Baltic Sea algal bloom [credit: Scitech Daily]





The CLAW hypothesis proposes a negative feedback loop that operates between ocean ecosystems and the Earth’s climate.[1] The hypothesis specifically proposes that particular phytoplankton that produce dimethyl sulfide are responsive to variations in climate forcing, and that these responses act to stabilise the temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere. The CLAW hypothesis was originally proposed by Robert Jay Charlson, James Lovelock, Meinrat Andreae and Stephen G. Warren, and takes its acronym from the first letter of their surnames. [bold added].
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/CLAW_hypothesis
“Science is the belief in the ignorance of the experts” – Richard Feynman
And they regularly demonstrate it – “The (climate) science is settled.” QED.
From 2008
“John Dacey, a biologist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), is one of the few marine scientists who have devoted a great deal of time to studying oceanic DMS over the past few decades. He says he’s amazed and dismayed that carbon dioxide receives so much research funding right now at the expense of other basic science, when other gases may have critical roles to play in countering or augmenting warming.”
https://www.whoi.edu/oceanus/feature/dms–the-climate-gas-youve-never-heard-of
Seems nothing much ever changes when you have already “Settled Science”
Woods Hole 2008: If DMS production is speeded up by global climate change, as many scientists believe it will be, then it could provide a cooling effect. That means DMS could help offset greenhouse warming.
So the UEA ‘discovery’ is only 16 years out of date.
To Oldbrew, the current paper ” Co-lead author Professor Jonathan Todd, of UEA’s School of Biological Sciences, said, “The Pelagophyceae are among the most abundant algae on Earth, yet they were not previously known as important producers of DMSP. “
“not previously known”? Strewth Lovelock was pontificating about them in the 1980s
Maybe UEA are lining them up as an excuse for the lack of supposed CO2 effects. This study proves they knew about DMS at least as far back as 2010.
Can we trust empirical marine DMS parameterisations within projections of future climate?
P. R. Halloran1, , T. G. Bell2, , and I. J. Totterdell1
1Met Office Hadley Centre, FitzRoy Road, Exeter, Devon, EX1 3PB, UK
2University of East Anglia, Norwich, NR4 7TJ, UK
Published: 20 May 2010
Plain Language Summary
The trace gas dimethyl sulfide is a precursor for natural, sulfur-based aerosols that influence climate, an important compound in marine microbial communities, and an olfactory foraging cue for seabirds. This article discusses data from two surveys of dimethyl sulfide in 2010 and 2011 in the Subarctic Northeast Pacific ocean. [etc]
Click to access bg-7-1645-2010.pdf
Think about Fe fertilization as a supercharging element in this.
Where does Fe come from to accelerate this growth. The two areas are volcano’s and fires also possibly human fertilization as proposed by Dr Martin but as yet illegal however it works.
So we suppress fires and the oceans emit less DMS possibly billions of tons per year and the hapless fools talk about low sulfur oil in shipping.
The things to understand are Fe fertilization and cloud formation a further driver of what Willis E. has labeled the emergent phenomena.